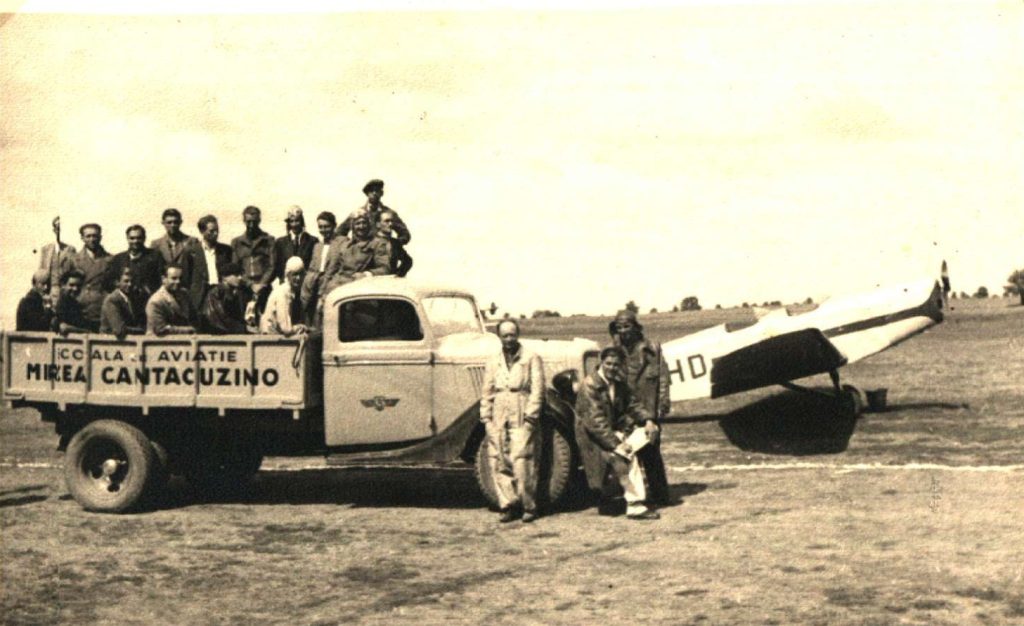
PZL P.24A fost un avion de luptă polonez, proiectat la mijlocul anilor 1930 în fabrica PZL din Warsaw. A fost exportat în câteva ţări dar nefolosit în Polonia.
Role: Fight
Maker: PZL
Designer: Zygmunt Puławski
First flight may 1933
Introduction 1936
Retras: 1960 Turkish Air Force
First users:
Turkish Air Force
Royal Romanian Air Force
Bulgarian Air Force
Hellenic Air Force
Developed from: PZL P.11
Variante: IAR 80
PZL P.24was a Polish fighter aircraft designed in the mid-1930s at the PZL factory in Warsaw. It was exported to several countries but not used in Poland.
Design and development
The PZL P.24 was designed as an export version of the PZL P.11, a "gullwing" fighter designed by Zygmunt Puławski. P.11 was started with a licensed Bristol Mercury engine. The license did not allow export sales. So the French company Gnome-Rhône proposes the use of their engines in the P.11. The first prototype P.24/I, based on the P.11a and designed by Gnome-Rhône 14Kds 760 hp 570 kW engine, flew in May 1933. The second prototype, P.24/II numit "Super P.24", set the world speed record for radial-engine fighter aircraft (414 km/h). The third prototype P.24/III it was "Super P.24bis" with a much more powerful 14Kfs motor. The model was presented at the 1934 Paris Air Show attracting the interest of many attendees.
The aircraft was conventional in layout, with high wings. It was all-metal and metal-covered. The wings had a gull-wing shape, with a thin profile close to the fuselage, to provide a good view for the pilot. This configuration was developed by Zygmunt Pulawski and called „the Polish wing”. The canopy was closed (apart from prototypes). An internal 360 liter fuel tank in the fuselage could be dropped in case of fire emergency. It had conventional fixed landing gear, with a rear skid.
The armament was a combination of 20 mm Oerlikon FF cannon and 7.92 mm Colt-Browning machine guns in the wings.
The P.24A, P.24E and P.24F had two cannons and two machine guns.
P.24B, P.24C and P.24G The 24G had four machine guns.
Operations history
Despite being a better fighter than the P.11, there were few acquired by the Polish Air Force, which preferred to wait for the PZL.50. When it became clear the PZL.50 would not be ready in time to counter the imminent German attack, the PAF resumed production of the P.11 and ordered the P.24. However, no PZL.24s were produced before the war started, and only two were used in the Polish Campaign. The aircraft had greater success abroad, though.
Turkey
Turkish P.24s were used for training until the late 1940s. Some were refitted with Pratt & Whitney Twin Wasp engines. The only surviving example of a PZL P.24 in the world is an example in Turkey. Photographs of the Turkish museum piece show a variety of serial numbering (2015, 2017, 2147) and are shot at different locations: (Ankara and Istanbul), suggesting that there may be more than one survivor.
Greece
The PZL P.24 was the main Greek fighter at a time of the Italian attack in 1940, and engaged Italian bombers during the Greco-Italian War.
Romania
The Romanian Air Force already used PZL P.11Fs built under license in the IAR factory, and decided to acquire the P.24 as well. Romania bought five P.24Es and a production license, and built 25 IAR P.24E aircraft at the IAR factory between 1937 and 1939. Some components of the P.24E, mainly its tail section, were used in construction of the Romanian low-wing fighter IAR 80. The fighters were used to guard Bucharest and the Ploieşti oilfields from Soviet bombers at the start of Operation Barbarossa. Flying from Otopeni military airbase, the PZL P.24 fighters managed to shoot down 37 unescorted VVS bombers. The P.24E was also used for ground attack missions until the end of 1941 and after 1942 it was relegated to training duties because of its obsolescence.
Variants
During the development of Pulawski fighters, a new version of the P.11, the P.11c, was developed for the Polish Air Force. It had a new, reconfigured fuselage, and the radial engine was lowered to give a pilot a better view. These changes were applied also to the new P.24 prototype, flown in 1936. The P.24A and P.24B models could carry 4 x 12.5 kg bombs, while the P.24C, F and G could carry 2 x 50 kg bombs.
P.24 – This design used the whole tail fuselage section from the P.11c, was powered with a Gnome-Rhône 14Kfs engine (930 hp), and was armed with two 20 mm cannon and two machine guns.
P.24A
It entered production as P.24A.
P.24B
The model P.24B it was armed with four machine guns.
P.24C
P.24C was armed with four machine guns and two 50 kg bombs.
P.24D
P.24D a fost dezvoltat pentru a fi vândut in Ungaria, dar nu a fost finalizat. Ungaria cumpărase deja Fiat CR.32.
IAR P.24E
The version P.24E had a construction license in Romania from IAR as IAR P.24.E
P.24F a fost înarmat cu două tunuri, două mitraliere și bombe și alimentat cu cel mai puternic motor Gnome-Rhône 14N-07 970CP (720 Kw)
P.24G Ultima versiune de producție a fost P.24G, produs din 1937 și dotată cu cel mai puternic motor Gnome-Rhône 14N-07 970 cp (720 kW), înarmat cu patru mitraliere și bombe.
P.24H was to be powered with a Gnome-Rhône 14N-21 engine (1,100 hp) and carry four cannon or two cannon and two machine guns, but it was not completed. The P.24H was considered for purchase by the Polish Air Force, but progress was slow due to the P.24’s similarity to the PZL P.11, which was already in service, and also interest in the hypothetically superior PZL.50 Jastrząb then under development. World War II started before any of these plans could be realized.
PZL P.24was a Polish fighter aircraft designed in the mid-1930s at the PZL factory in Warsaw. It was exported to several countries but not used in Poland.
Specificații (P.24C)
General characteristics
Crew: 1
Capacity fighter plane
Length: 7.81 m (25 ft 7 in)
Scope: 10.68 m (35 ft 1 in)
Height: 2.7 m (8 ft 19 in)
Bearing surface: 17.90 m² (192.7 ft²)
Empty weight: 1,330 kg (2,930 lb)
Weight with load: 1,915 kg (4,220 lb)
Weight with load: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb)
Motopropulsor group: 1 × Gnome-Rhône 14Kfs 14-cilindrii , motor radial double row , 900 hp / 930 cp (max) (671 kW / 693 kW (max)
Performances
Full speed: 430 km/h (270 mph)
Range: 550 km (340 mi)
Service ceiling: 10,500 m (34,449 ft)
Rate of climb: 11.5 m/s (2,260 ft/min)
Power/mass: 0.376 kW/kg (0.230 hp/lb)
Armament
4 MGs
2 x 50 kg (110 lb) bombe